
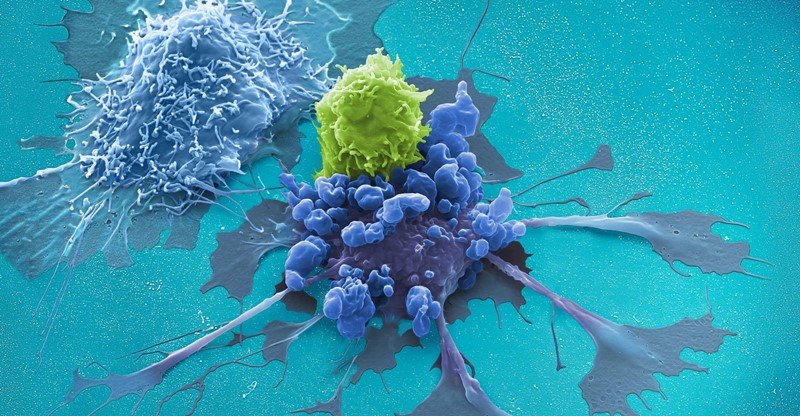
CD19 CAR T cells are the cell-therapy product used as the treatment for leukemia or lymphoma patients [1,2]. CD19 CAR T cells are developed from the genetic modification of patients’ T cells. Modified T cells express the receptors which can bind to CD19 protein expressed highly in leukemia and lymphoma cancer cells. This binding can induce the immune system of the patient to destroy cancer cells eventually [3].
The treatment of CD19 CAR T cells became well-known in 2012. A six years-old leukemia patient named Emily Whitehead is the first pediatric case who has successfully cured after she has been treated with CD19 CAR T cells. After the treatment with CD19 CAR T cells, Emily has been cancer-free for 10 years. In 2017, the first approval of CD19 CAR T cells have been approved by US FDA to use as a blood-cancer treatment [4]. This first approved product was registered by Novartis under the name of Kymriah [5]. Since then, many variations of CD19 CAR T cells have been registered from various company. For example, KitePharma has developed CD19 CAR T cells which has also been approved under the name Yescarta [6]. Additionally, there are many CAR T cells which are in clinical trials [7]. If they prove to be efficient ways of treatment in these trials, it will give more options of treatments to cancer patients. Hence, many believes that more patients will be treated with CAR T cells in the future.
References
[1] Davila ML, Brentjens RJ. CD19-Targeted CAR T cells as novel cancer immunotherapy for relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2016;14(10):802-808.
[2] Chavez JC, Yassine F, Sandoval-Sus J, Kharfan-Dabaja MA. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in B-cell lymphomas: current status and future directions. Int J Hematol Oncol. 2021;10(2):IJH33. Published 2021 Aug 3. doi:10.2217/ijh-2020-0021
[3] Davila ML, Bouhassira DC, Park JH, et al. Chimeric antigen receptors for the adoptive T cell therapy of hematologic malignancies. Int J Hematol. 2014;99(4):361-371. doi:10.1007/s12185-013-1479-5
[4] Emily Whitehead Foundation. 2022. Our Journey | Emily Whitehead Foundation. [online] Available at: <https://emilywhiteheadfoundation.org/our-journey/> [Accessed 27 May 2022].
[5] U.S. Food & Drug Administration: KYMRIAH (tisagenlecleucel); 2017 August 30th. Available from https://www.fda.gov/biologicsbloodvaccines/cellulargenetherapyproducts/approvedproducts/ucm573706.htm
[6] U.S. Food & Drug Administration: YESCARTA (axicabtagene ciloleucel); 2017 October 18th. Available from https://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/ucm581222.htm
[7] Safarzadeh Kozani P, Safarzadeh Kozani P, Rahbarizadeh F. Novel antigens of CAR T cell therapy: New roads; old destination. Transl Oncol. 2021;14(7):101079. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101079